Resilience of grassland plant communities as influenced by root herbivores under different land use intensities
Ecosystem resilience is an essential factor underlying the sustained production of natural resources and ecosystem services in complex systems faced with uncertainty and surprise. Root herbivory can have significant impact on grassland productivity and biodiversity under constant conditions. However, there is yet no knowledge on root herbivory impact on plant community recovery after disturbances, short-term stresses or nutrient pulses. Our project aims at assessing the role of root herbivory in plant community resilience under different land use intensities.
Root herbivore effects on grassland resilience depend on:
- the nature of root herbivory
including intensity / timing / distribution / feeding preference
e.g. feeding preference for abundant plant species promotes recovery of species diversity - the nature of disturbance/stress
affecting predominantly plants / affecting also root herbivores / promoting dominance
of specific plant species
e.g. comprehensive stress that affects not only plants but also root herbivores generates a
lag phase in root herbivore activity and weakens their impact - the nature of the system
including plant diversity / nutrient level
e.g. root herbivory has strong effects in nutrient rich systems due to its impact on
competition for space
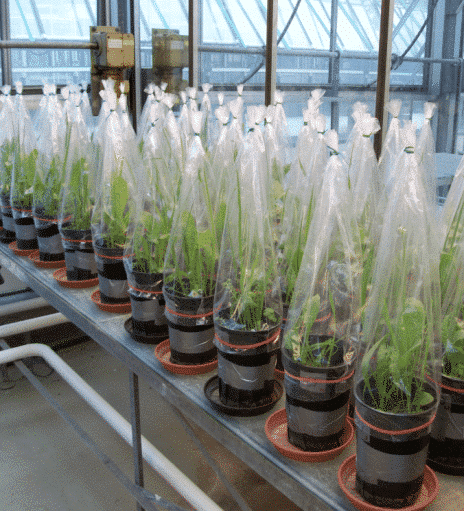
Exploring the dynamic interactions and feedbacks between root herbivores and grassland plant communities after different types of disturbances and stresses requires a mechanistic approach. We will determine general aspects of root herbivore impact on plant community recovery in controlled greenhouse experiments and monitor plant and root herbivore abundance and community composition after disturbance/stress in field surveys. In addition, we will develop and apply process-based simulation models of both, root herbivores and the plant community. In a next step these models will be coupled to systematically investigate the role of plant-herbivore interactions for the resilience of the coupled system. We will focus on root herbivory by click beetle larvae of the genus Agriotes as widespread and abundant generalist root herbivores in European grasslands.