Impact of Agricultural Land Use Intensity on the Health Functions of Microbiome along the Food chain
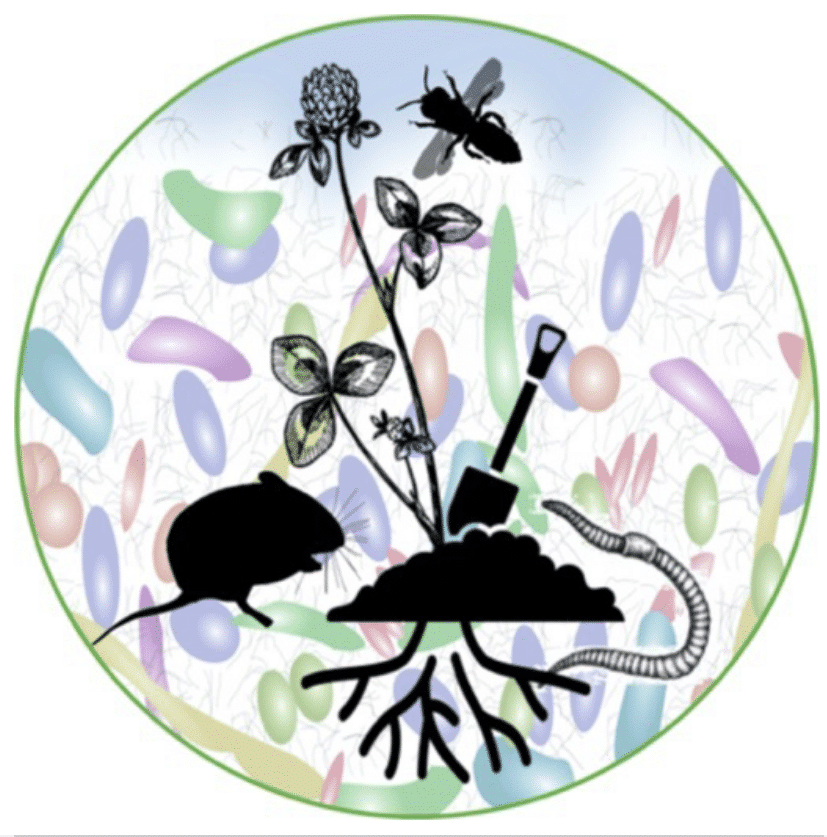
The common goal of the IMPALA project and the DFG exploratories is to understand the impact of land use changes on diverse aspects of biodiversity, ecosystem services and environmental health. In the IMPALA project, funded by the Baden-Württemberg Foundation, we will investigate the impact of agricultural land use intensification through the use of different fertilizers on the microbiome and its functional interactions with hosts along a trophic cascade in grassland ecosystems. The main objectives are to determine the influence of different fertilizer regimes on the function of soil, root and inflorescence microbiomes using Trifolium pratense as an example, and in the gut of soil-digesting earthworms, herbivorous voles and pollinating insects. Genes for antibiotic resistance and production of natural antimicrobial peptides, so-called bacteriocins, serve here as metrics for the function of a microbiome. The project thus provides important information on the effects of fertilization on the stability of an ecosystem, mediated by host-microbiome interactions.
To this end, data will be collected on the following parameters:
- Microbiome data from clover plants (root zone and inflorescences).
- Microbiome data from the gut of earthworms
- Microbiome data from the gut of voles
- Microbiome data from pollinating insects
More information about this project can be found here: https://www.uni-ulm.de/nawi/nawibiologie/wissenschaft-forschung/impala/