Elemental cycling in forests and grasslands of Biodiversity Exploratories: Response to management intensity and biodiversity
Element fluxes respond far more rapidly to changing environmental conditions (including land use change and reduced biodiversity) than the soil fixed phase or the forest stand itself. Therefore, the study of element fluxes is a suitable means to elucidate the influence of land use intensity and biodiversity on the functioning of forest and grassland ecosystems of Biodiversity Exploratories. While it is already known that different land use types (such as forest or grassland) have strong effects on element cycles, the consequences of different intensities of management of the same land use type and the associated biodiversity for element cycles in established, real-use ecosystems are still largely unknown.

Element and nutrient budgets of ecosystems include inputs (atmospheric deposition, fertilisation), internal cycles (mineralisation, weathering, uptake by biomass, translocation, accumulation) and outputs (leaching, gaseous emissions, crop removal). A large part of the conversion and mass transport takes place in dissolved form in precipitation and soil solution. For both the provision and the retention of nutrients, processes in the soil and in the canopy are of particular importance and therefore receive special attention. Many of these processes are biological in nature and it is assumed that synergies through higher biodiversity favour the internal recycling of elements and nutrients, thus reducing nutrient losses.
To help elucidate the drivers of stable ecosystem functions and resulting ecosystem services, we are investigating water flows and nutrient cycling from different forest and grassland management systems of varying biodiversity in each of the three exploratories (56 experimental plots in total).
1. Nutrient inputs and outputs of ecosystems and element cycling are linked to land use intensity and biodiversity.
2. losses of nutrients and carbon with leachate are inversely proportional to land use intensity and biodiversity of forest and grassland ecosystems.
3. the conversion and recycling of carbon compounds in ecosystems leads to an equalisation of the quality of dissolved organic matter of different ecosystems along the water flow path from the canopy to the subsoil.
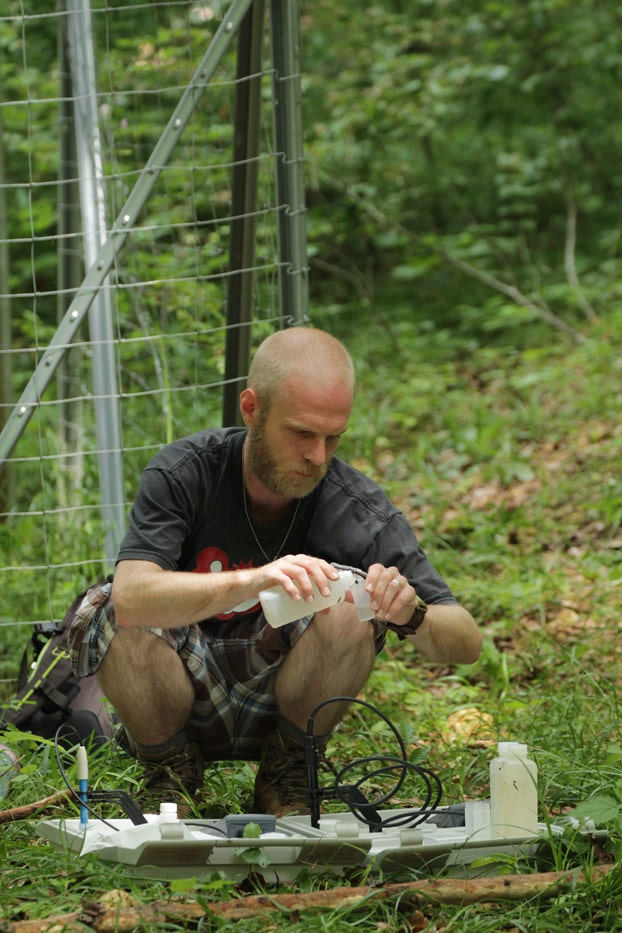
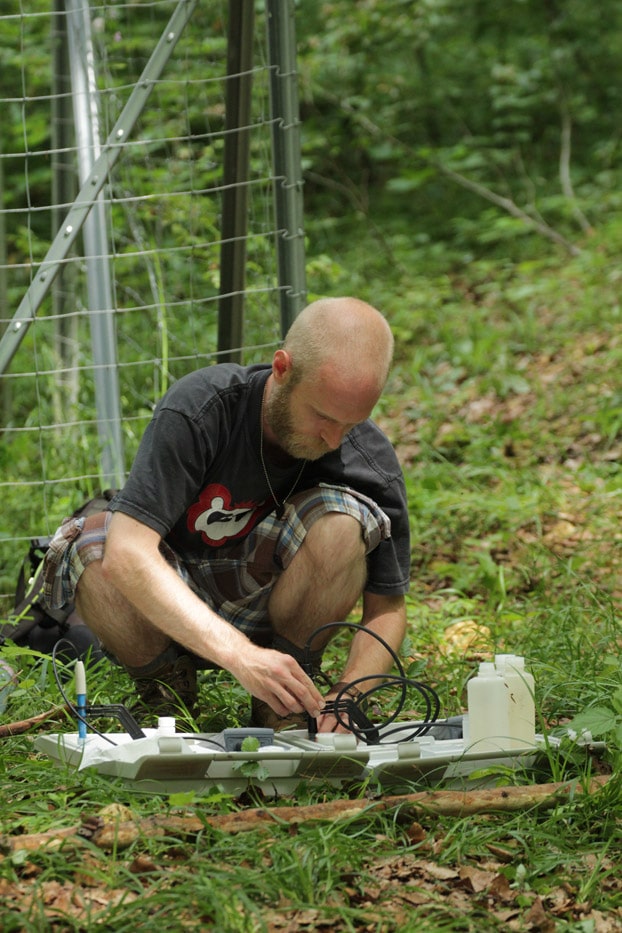
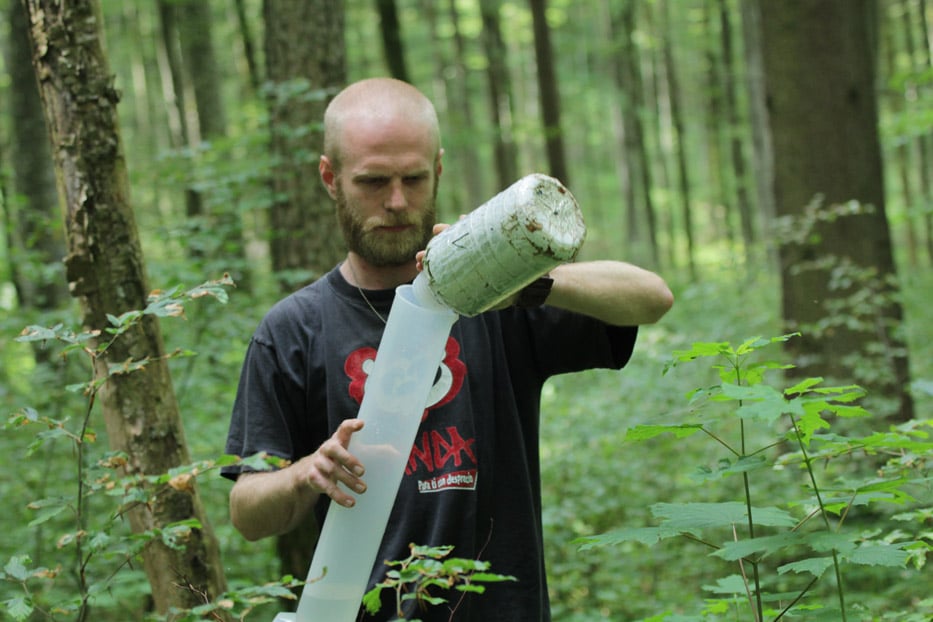
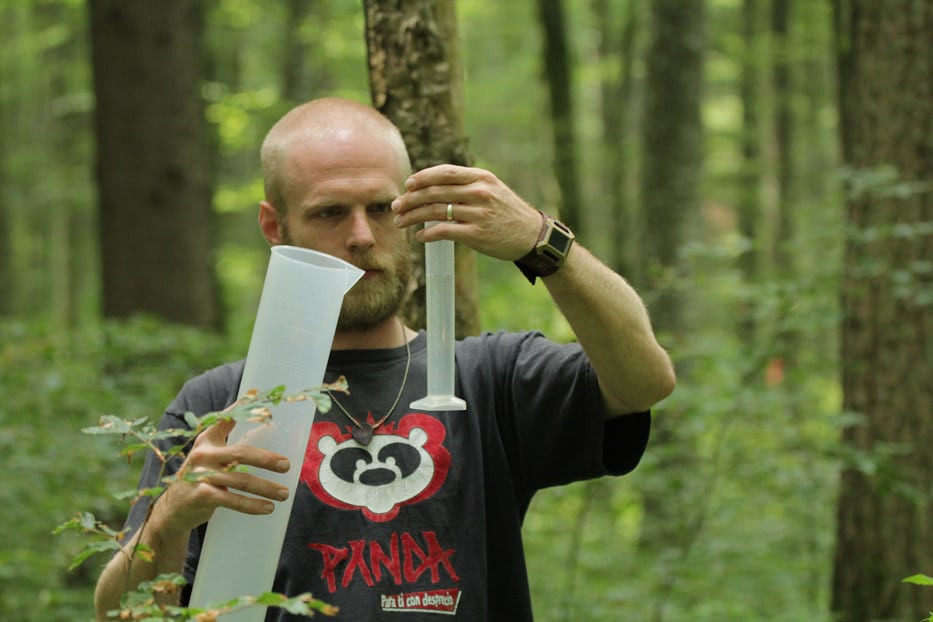
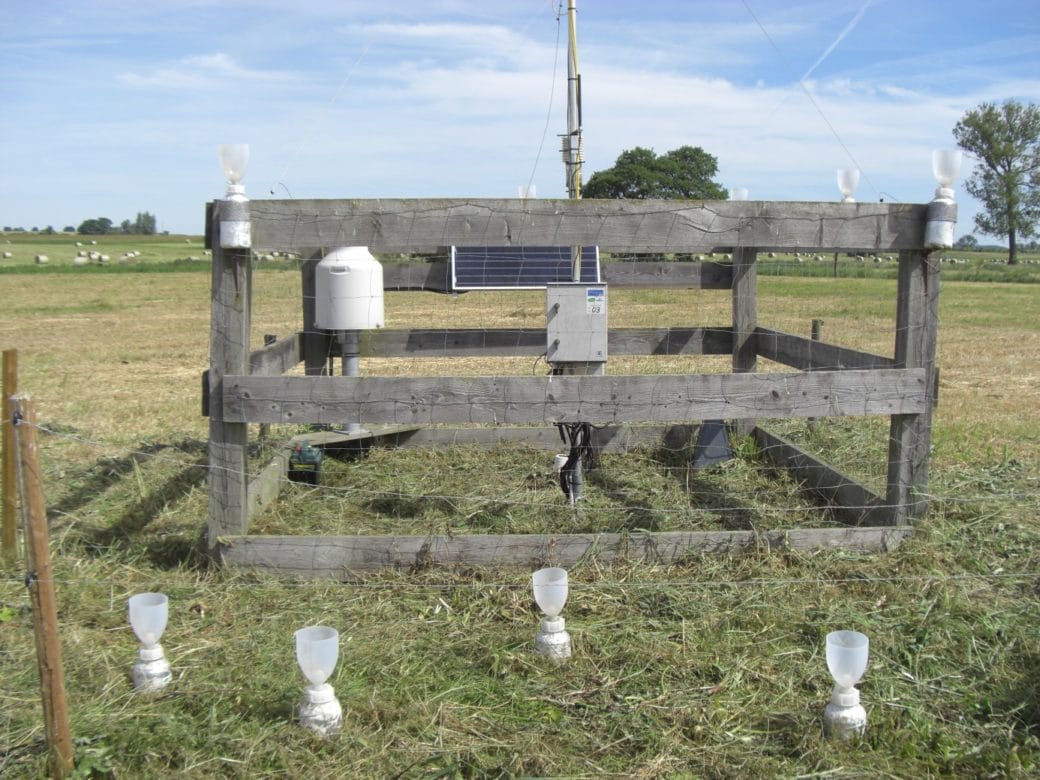
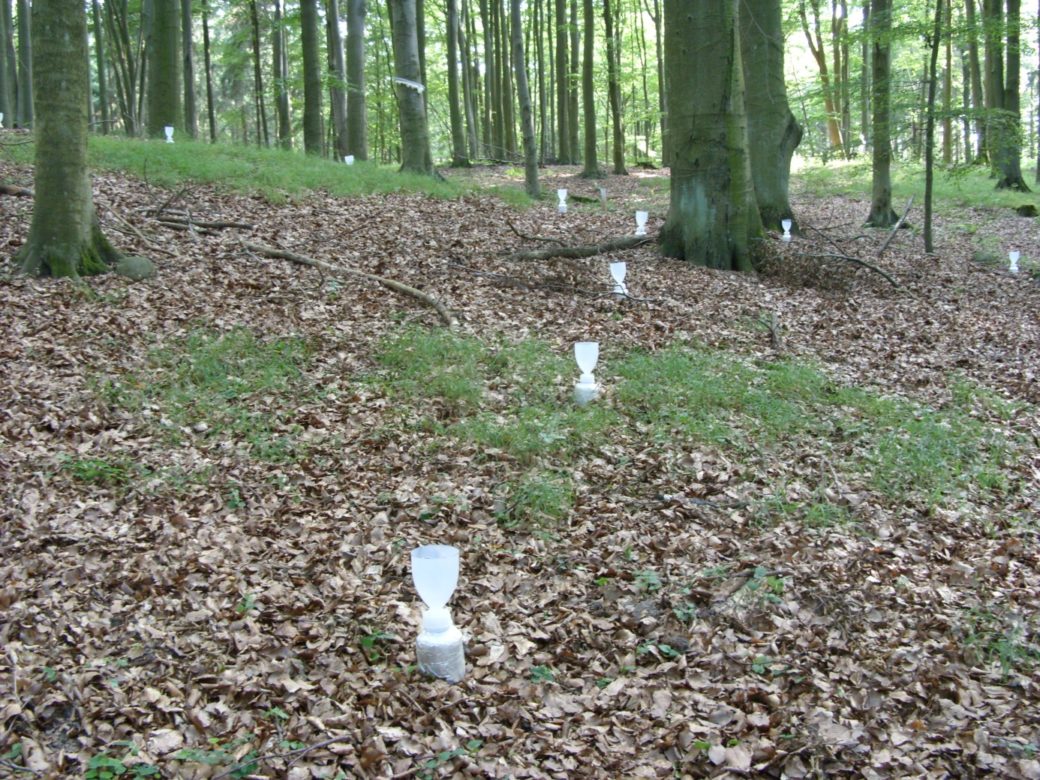
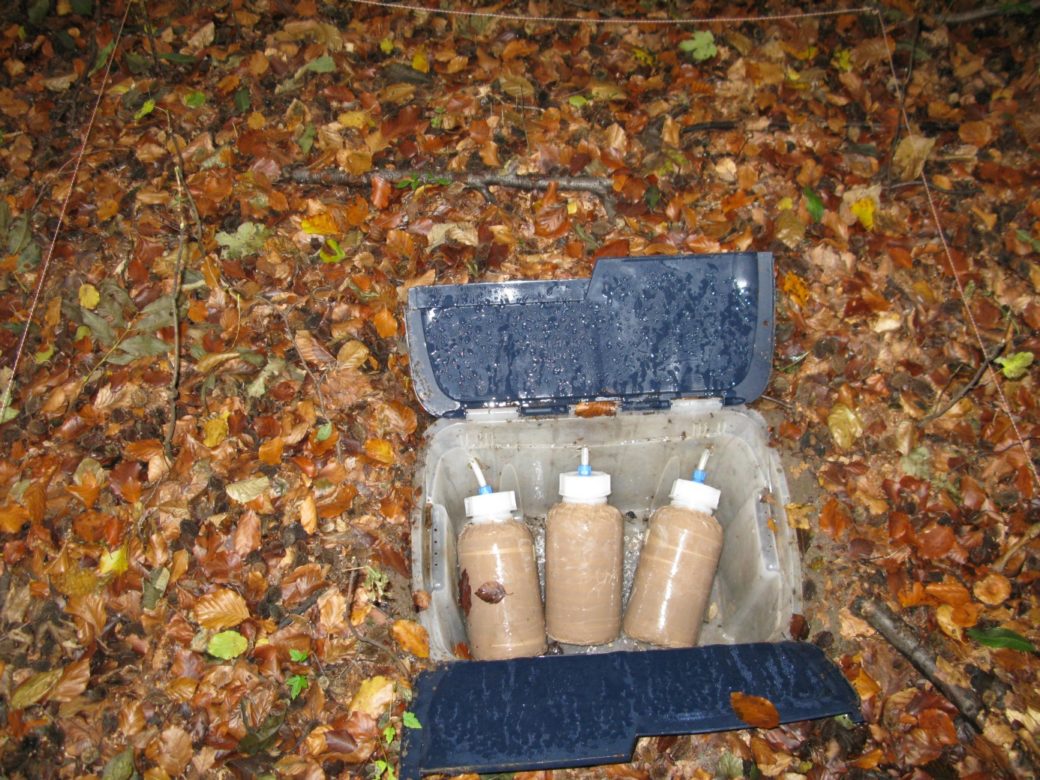
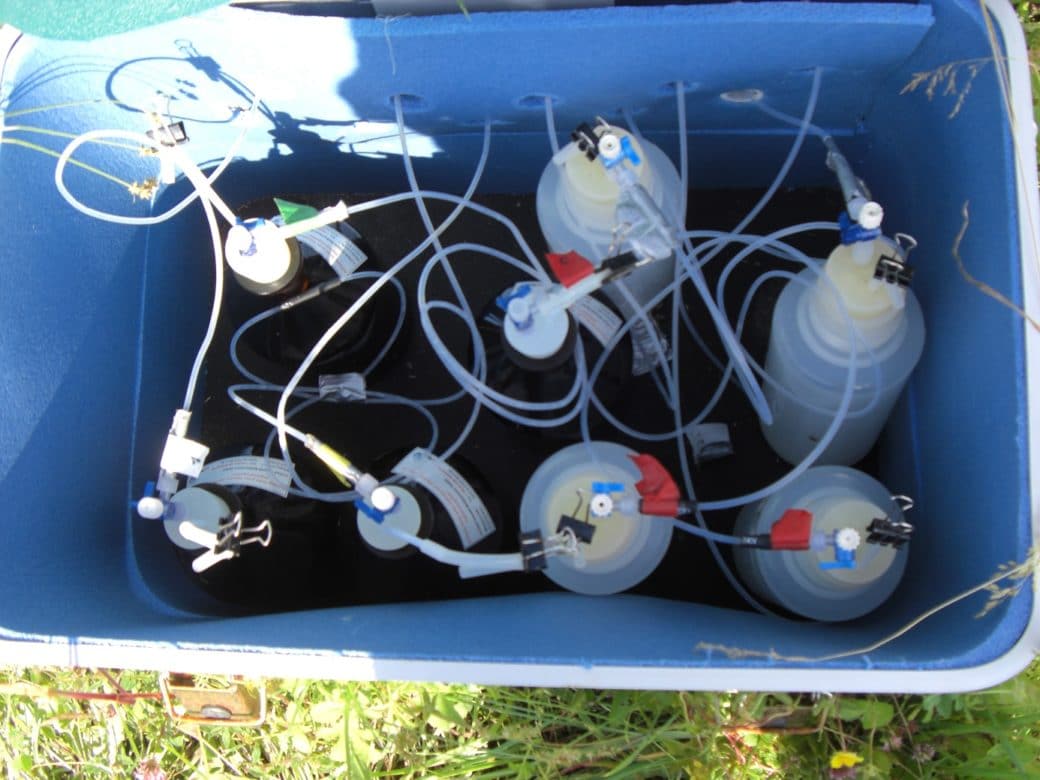
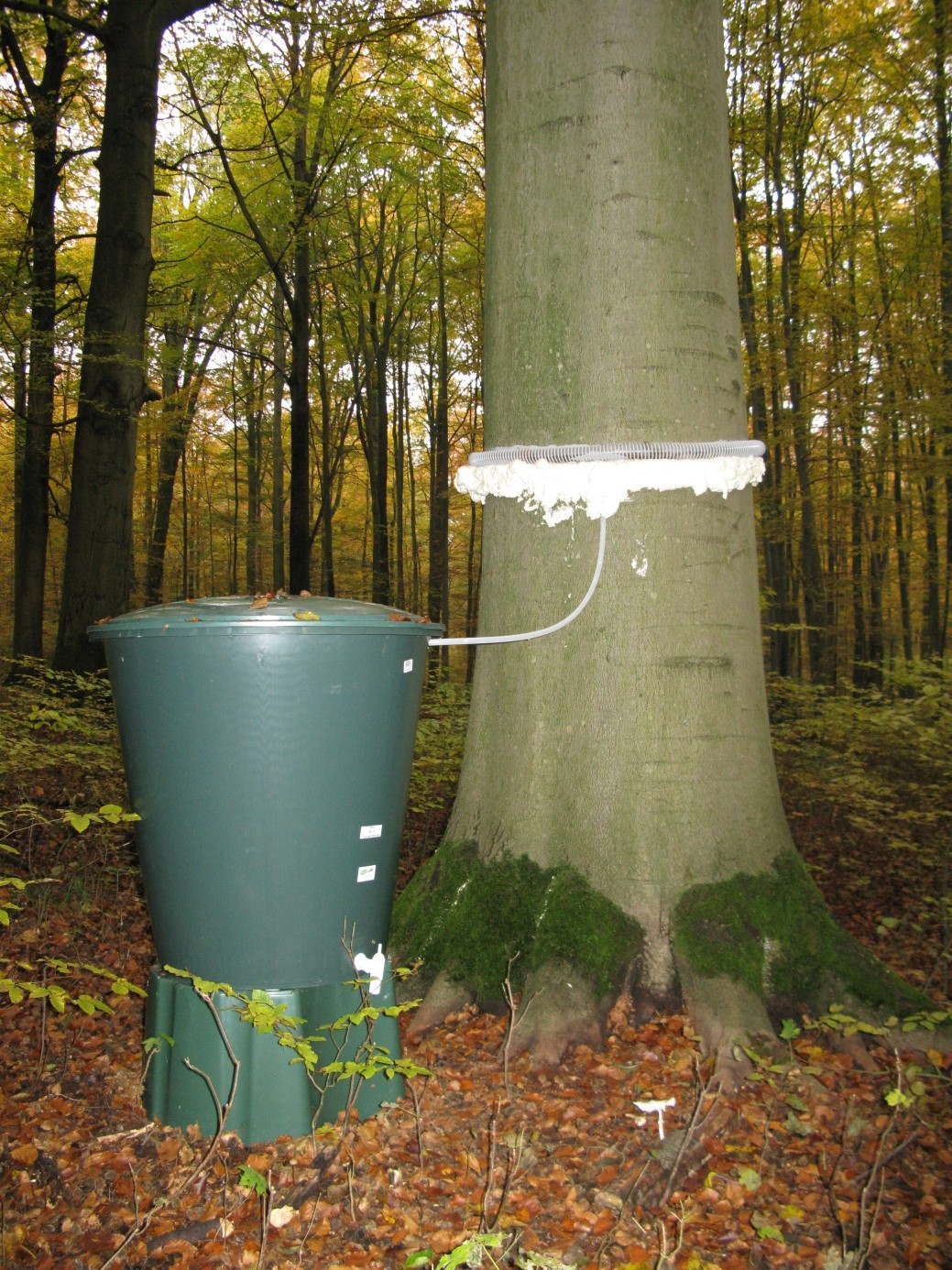
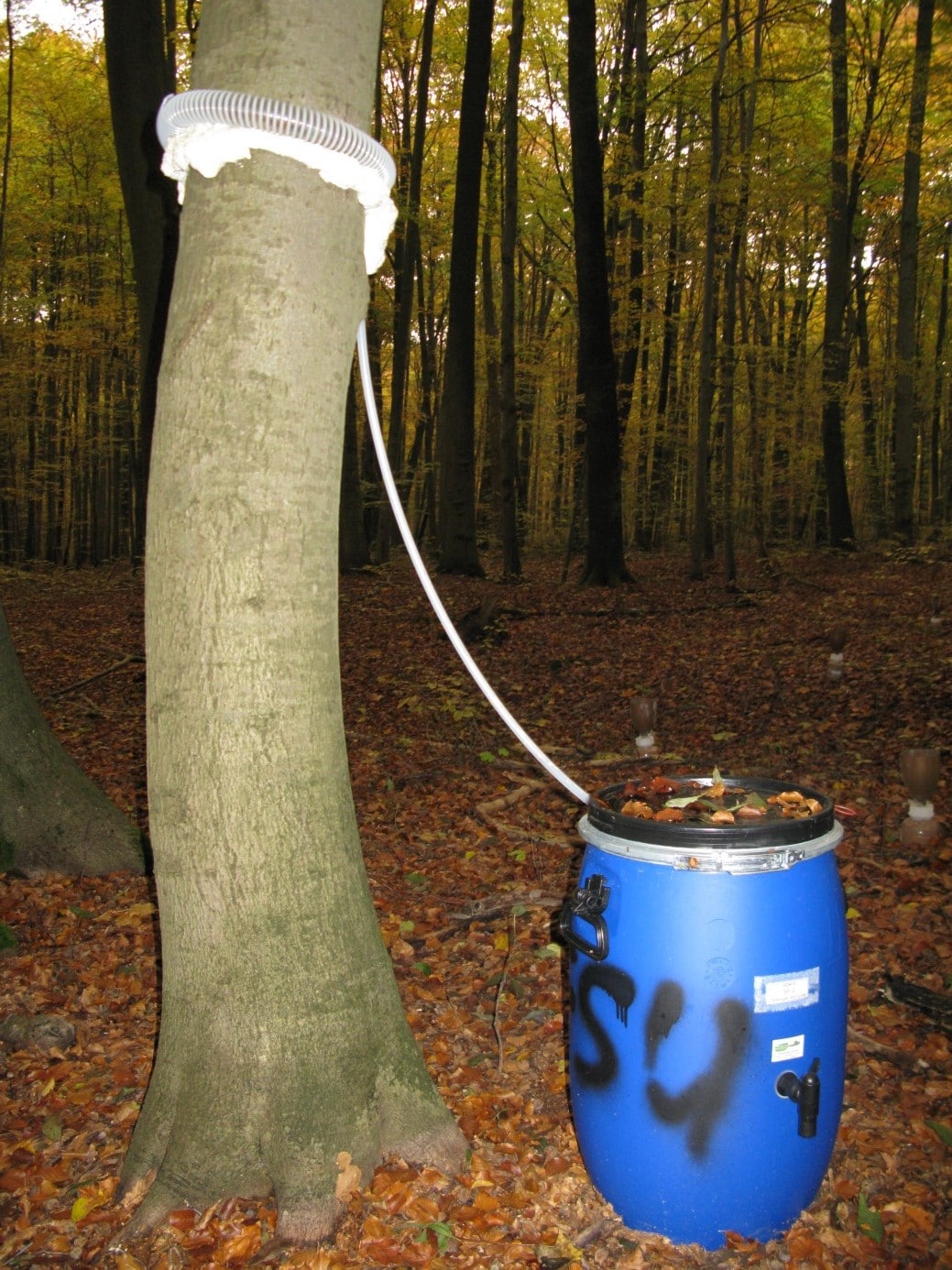
For this purpose, outdoor precipitation, stand precipitation and stemflow collectors as well as litterfall collectors were set up to record both atmospheric substance input and conversion processes in the canopy. Conversions in the soil and losses with the seepage water are elucidated with the help of lysimeters under the organic forest soil layers and suction candles.
In the aqueous solutions obtained, we determine concentrations of various C (dissolved inorganic carbon = DIC, dissolved organic carbon = DOC, particulate organic carbon = POC), N (dissolved nitrogen = DN, particulate nitrogen = PN, NH4-N, NO3-N) and P species (total phosphorus = TP, PO4-P), as well as elements such as S, Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al, Mn and Si. The characterisation and determination of the quality of dissolved organic matter (DOM) is carried out by FT-ICR-MS, fluorescence measurements and titration microcalorimetry, turnover of nutrients and their sources are investigated by stable isotope approaches (15N). Investigations of 15N signals on deciduous and coniferous tree leaves using nano-secondary ion mass spectrometry (NanoSIMS) will provide information on the formation and spatial distribution of particulate N compounds and other nutrients in the microbially colonised leaf space of trees. In addition, the composition of the microbial phyllosphere community will be investigated molecularly in cooperation with the Chair of Aquatic Geomicrobiology (FSU Jena).
The results of our investigations are a prerequisite for separating land use and biodiversity effects from each other and evaluating them in terms of their impact on material cycles.